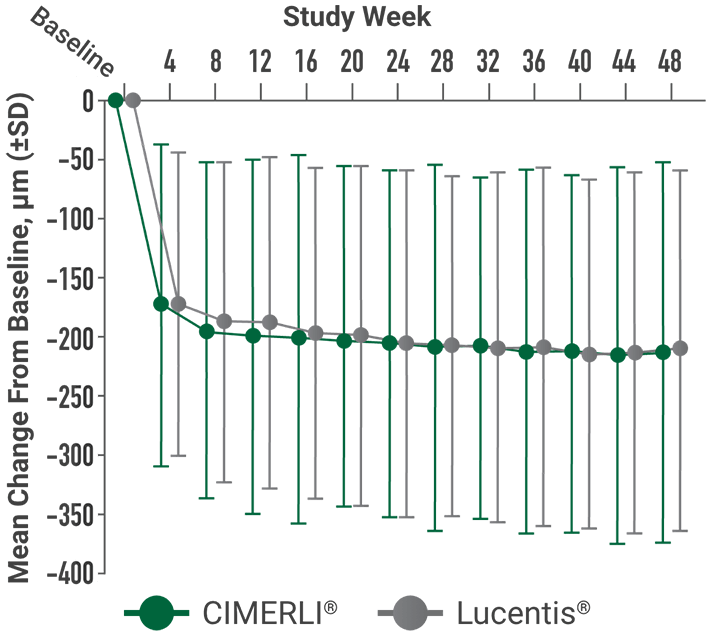
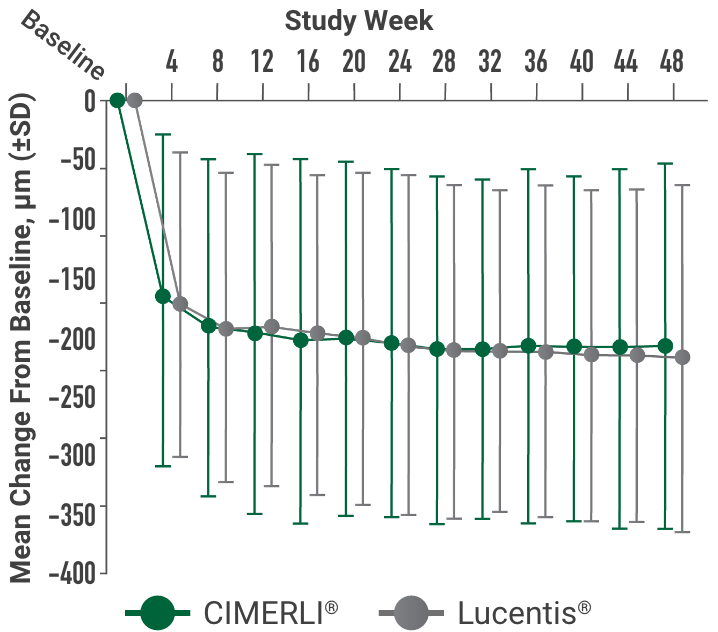
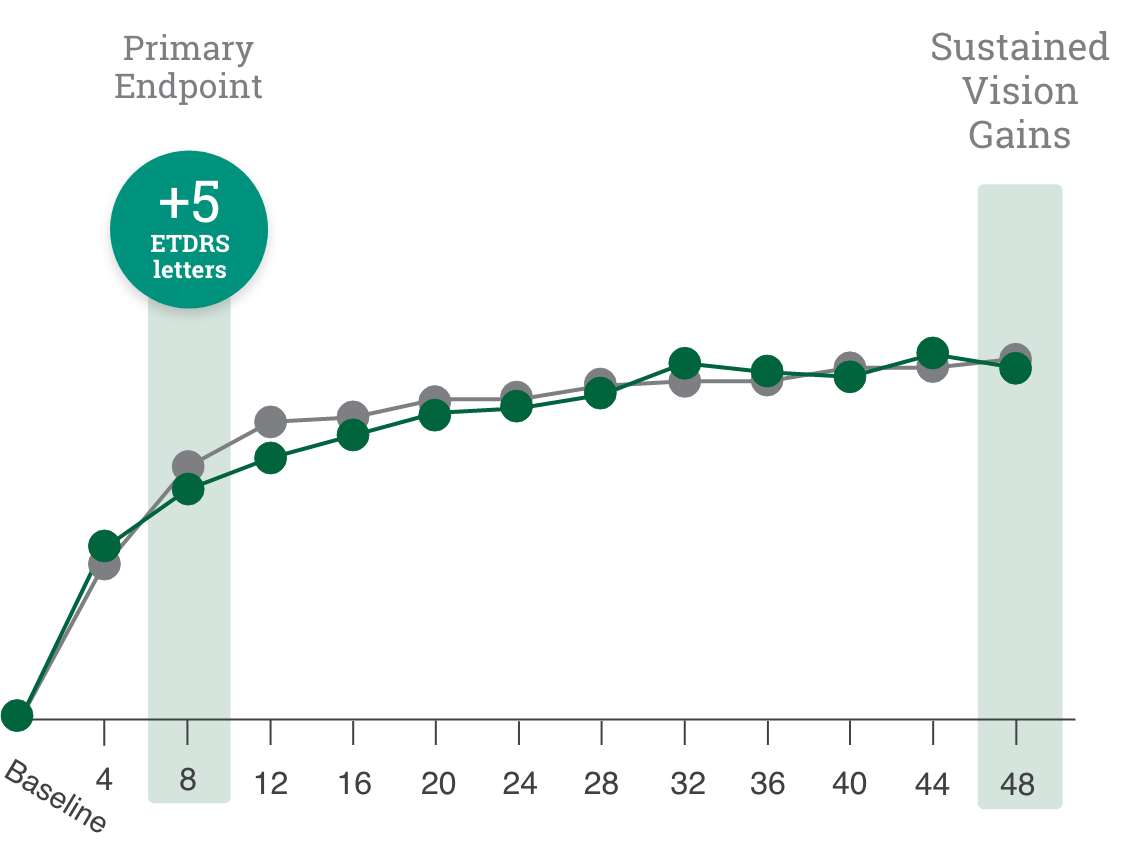
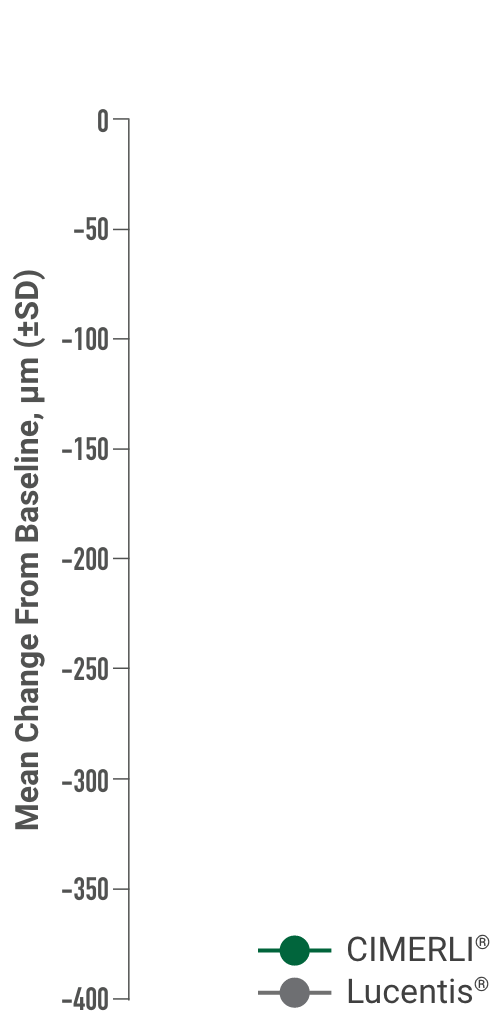
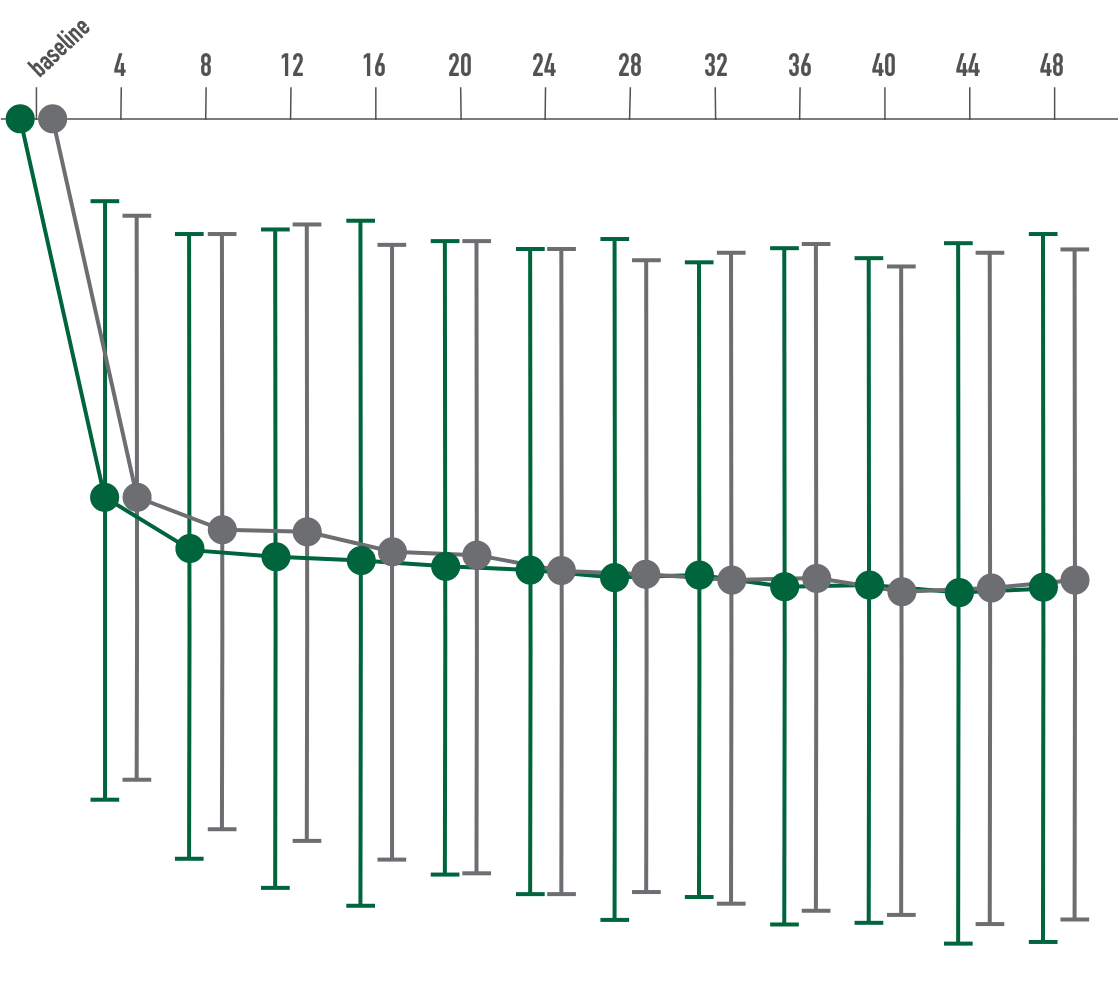
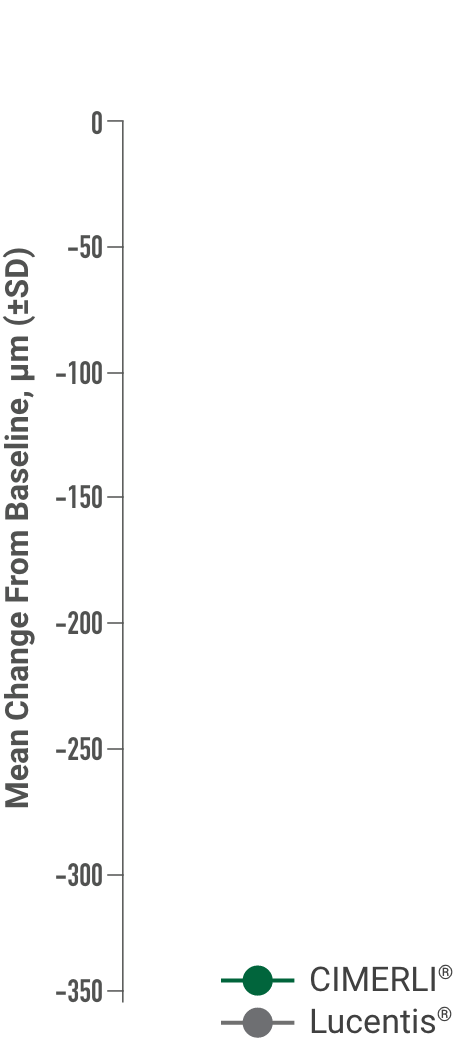
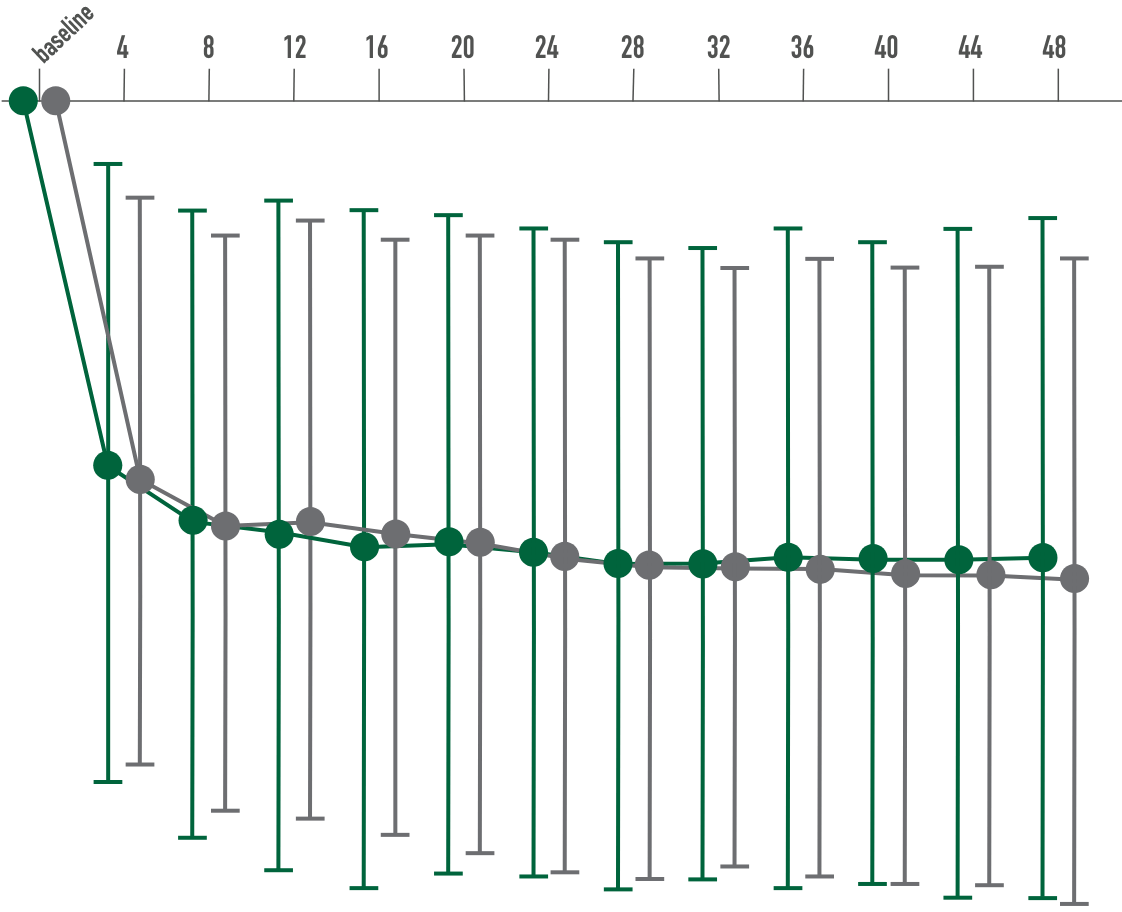
Primary endpoint:
BCVA improved in both CIMERLI® and Lucentis® treatment groups with an average of 5 more ETDRS letters at 8 weeks.
Secondary endpoint:
BCVA improved in both CIMERLI® and Lucentis® treatment groups with an average of 8 more ETDRS letters at 48 weeks.